Test Methods
DRP is a USACE accredited laboratory for petrographic examination and analysis of aggregate materials and hardened concrete. Materials that commonly find their way to our shop include:
- Ready-Mixed and Precast Concrete
- Plain & Reinforced Concrete
- Post-Tensioned & Prestressed Concrete
- Concrete Masonry Units
- Brick & Manufactured Stone Products
- Modern and Historic Masonry Mortars
- Shotcrete
- Grout
- Aggregate Resources
- Natural Rock & Stone Products
- Terrazzo & Decorative Concrete
- Sealants & Membranes
We most commonly perform the following tests:

ASTM C295: Standard Guide for Petrographic Examination of Aggregates for Concrete
This examination identifies the rocks and minerals present in coarse and fine aggregates. At least 150 particles are identified for each sieve size in a gradation. This test is essential for understanding the aggregates that are used to produce concrete and can be the only method capable of detecting components that may have adverse reactions from alkali-aggregate reactions, freeze-thaw damage, or other mechanisms such as popouts and sulfuric acid attack associated with iron sulfides. Click here to see the standard.
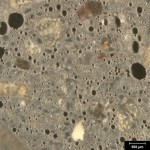
ASTM C457: Standard Test Method for Microscopical Determination of Parameters of the Air- Void System in Hardened Concrete
This test is the most widely accepted method for determining the air content and parameters of the air-void system in hardened concrete. The test provides key information on not only how much air is present, but whether the size and spacing of the voids are suitable for providing protection against freeze-thaw damage. At DRP we measure paste and aggregate content in addition to air content, which allows us to trouble-shoot concrete mixtures for strength issues as well as freeze-thaw durability issues. Click here to see the standard.
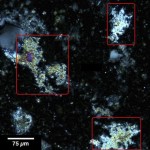
ASTM C856: Standard Practice for Petrographic Examination of Hardened Concrete
This is the industry standard throughout the world for investigating a multitude of problems. The scope of the standard lists more than twenty different purposes for the examination. In brief, these may include determining whether the concrete complies with mix design submittal information and job specifications, trouble-shooting strength issues and determining if aspects of workmanship such as consolidation, finishing, and curing, are adequate. Petrography is also the only accepted method to determine if concrete is undergoing progressive deterioration from mechanisms such as alkali-silica reaction, sulfate attack, chemical attack, corrosion, early freezing, freeze-thaw damage, and more. Click here to see the standard.

ASTM C1324: Standard Test Method for Examination and Analysis of Hardened Masonry Mortar
This test involves a combination of petrographic analysis per ASTM C856 and additional chemical analysis. This combination of techniques affords an opportunity to determine the composition of the type of mortar (M, N, S and O) as described in ASTM C270, Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry. The test method is also used for understanding mortar compositions in historical structures where preservation and restoration are the priority. Click here to see the standard.
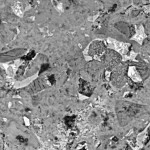
ASTM C1723: Standard Guide for Examination of Hardened Concrete Using Scanning Electron Microscopy
Higher magnification. Superior resolution. In situ chemical analysis. These attributes make the scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive x-ray spectrometer (EDS) an ideal instrument for supplementing nearly all of the investigations described in the scope of ASTM C856. We house a state-of-the-art FEI Quanta 250 Environmental SEM configured with an EDAX Apollo silicon drift detector EDS. Click here to see the standard.
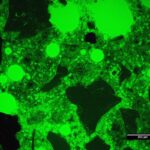
NT Build 361: Concrete, Hardened Water-Cement Ratio
Water-cement ratio (w/c) and water-cementitious materials ratio (w/cm) are critical parameters for assessing the quality and potential durability of concrete mixtures. This method was developed in Denmark in the 1980s and is used widely throughout Europe. We use vacuum impregnation with fluorescent epoxy to prepare thin sections for estimating w/c and w/cm.

ASTM C1152: Standard Test Method for Acid-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete
Acid soluble chloride testing is crucial for investigations where corrosion of steel reinforcement is a concern as well as scaling investigations where deicing salts are a potential factor. These analyses capture the total amount of chloride in the concrete. We perform multiple analyses on cores to establish chloride profiles that we combine with other testing capabilities to provide clients with service life models based on corrosion of reinforcing steel.

ASTM C1218: Standard Test Method for Water-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete
Water-soluble chloride analyses measure the concentration of chlorides that are not bound to the cementitious matrix. Such chlorides initiate or accelerate the corrosion of steel reinforcement and are another important component of service life modeling

ASTM C1876: Standard test for Bulk Electrical Resistivity or Bulk Conductivity of Concrete
Bulk electrical resistivity is a powerful tool for measuring the transport properties of concrete, or how easily external agents may infiltrate and migrate through concrete. Bulk resistivity is used to calculate the Formation Factor of cementitious mixtures, which is an innovative way to measure transport properties of cementitious mixtures. Bulk resistivity is related to water to cement ratio and the addition of supplementary cementitious materials, so it is also be a valuable tool for quality control, particularly when combined with fluorescence microscopy. We also use bulk resistivity to measure the progression of damage from durability mechanisms such as alkali-aggregate reaction.
Questions? We have answers. Contact us.
Give us a call at 303.938.0166 to get your project rolling.
